Start/stop/restart mail router
Stop/start/restart router
tell router quite
load router
DA->server->Status->Server tasks->right click router->Stop/start/restart task
Recalculating the server's routing table
By default, at intervals of approximately 5 minutes, or after you restart the task, the router examines the Domino Directory for changes that would warrant rebuilding the routing table.
Force update the server's routing table.
Tell router update config
(The router checks the server , server configuration, connection, Adjacent and Non-Adjacent domain documents, and the Notes.in file for changes that might effect the routing topology. The Router then builds a new router table that incorporates that changes. The router repocess any messages currently in mail.box based on the new routing table)
Notice:
The email message will be hold on mail.box when you send email ,if the router has been stopped.
Router configuration example
Use one server for all Internet messages


The following is the configuration steps. (You can find the details of every step on the following document)
1)Enable "SMTP used when sending message outside of the local internet domain" for Mail2
2)Enable SMTP listener task for Mail2
3)Set up DNS correctly to list Mail2 as the connecting server for domain for inbounding mail
4)Enable "SMTP allowed outside of the local internet domain" for Mial1 & Mail3 and listing Mail2 as relay host. (Mail1 & Mail3 use SMTP to transfer message to Mail2)
Or Create a Foreign SMTP Domain document and SMTP connection document that define the route to Mail2 (This way Mail1 & Mail3 use notes routeing to transfer to Mail2)
Use separate servers for inbound and outbound Internet mail

1)Enable "SMTP used when sending message outside of the local Internet domain" for Mail2
2)Enable SMTP listener task for Mail3
3)Set up DNS correctly to list Mail3 as the connecting server for domain for inbounding mail
4)Enable "SMTP allowed outside of the local Internet domain" for Mail1 and listing Mail2 as relay host. (Mail1 use SMTP to transfer message to Mail2)
Or Create a Foreign SMTP Domain document and SMTP connection document that define the route to Mail2 (This way Mail1 use notes routing to transfer to Mail2)
Use two servers to balance Internet mail load

1)Enable "SMTP used when sending message outside of the local Internet domain" for Mail1 & Mail3
2)Enable SMTP listener task for Mail1 & Mail3
3)Set up DNS correctly to list Mail1 & Mail3 as the connecting server for domain for receive inbound mail
4)Enable "SMTP allowed outside of the local internet domain" for Mial2 & Mail4 and listing Mail1 & Mail3 as relay host. (Mail1 use SMTP to transfer message to Mail2)
Or Create a Foreign SMTP Domain document and SMTP connection document that define the route to Mail1 or Mail3 (This way Mail1 use notes routing to transfer to Mail2)
Use SMTP to route mail within the local Internet domain

1)Enable SMTP listener task for Mail1 Mail2 & Mail3
2)Enable "SMTP allowed within the local internet domain" for "MIME message only" for Mail1 Mail2 & Mail3
3)Either having all three server sin same Notes name network or Enable "Servers within the local Domino domain are reachable via SMTP over TCPIP" for each server.
4)Enter the server's Fully quality internet host name field on the Basic tab of the server document,. The local Router uses the value in this field to define the local internet domain in the absence if a Global Domain document. Other Domino servers on the network check this field before attempting inbound SMTP connections to this server. If the field is blank or contains an invalid value, all inbound mail transfers take place over Notes routing.
Notice
The servers must be in the same Notes named network, based on TCP/IP
Mail routing between a third-party server and Domino in the same Internet domain
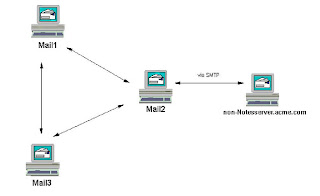
1)Enable the SMTP listener task for Mail2
2)Set up DNS correctly
3)Create a Foreign SMTP Domain document for "*.non-Notesserver.acme.com" and SMTP connection document that links to mail2.
4)Enable "SMTP used when sending messages outside of the local Internet domain″
(If the recipient has a mail file on the third-party server, non-Notesserver.acme.com, their Person document has a forwarding address with the domain ″non-Notesserver.acme.com.″ To route mail over SMTP, Mail1 and Mail3 find a Foreign SMTP Domain document for ″*.non-Notesserver.acme.com″ that corresponds to an SMTP Connection document listing
Mail2 as the server to which to transfer messages. The server sends the message via Notes routing toMail2, which has the field ″SMTP used when sending messages outside of the local Internet domain″enabled on the Router/SMTP-Basics tab of the Configuration Settings document that applies to it. If the message is in Notes format, Mail2 converts it to MIME. Mail2 connects to non-Notesserver.acme.com over TCP/IP and transfers the message over SMTP.
If a user on non-Notesserver.acme.com sends a message to a user on Mail1, Mail2, or Mail3, the server transfers the message over SMTP to Mail2, which has the SMTP listener task enabled on the Basics tab of its Server document, and Mail2 routes the message to its destination over Notes routing.) Use a smart host

1)Set up DNS correctly
2)Enable "SMTP allowed within the local internet domain" for "MIME messages only" for Mail1 Mail2 & Mail3
3)List "smarthost.acme.com" as the "Lcal internet domain smart host" for Mail1 Mail2 & Mail3.
Use all servers to route outbound mail and one to route inbound mail

1)Enable "SMTP used when sending message outside of the local Internet domain" for all three servers.
2)Enable the SMTP listener task for Mail2
3)Set up DNS corredtly to list Mail2 as the connecting server for the acme.com domain for inbound mail.
Create a configuration settings document.
Configuration settings document includes settings thar affect both Notes routing and SMTP routing.
Each server checks the cofiguration settings document in the following order-- a document specific to the server, then a group document for any group the server is in, and then for the default document.
DA->Configuration->Messaging->Configuration->Add configutration->Create a new configuration settings document->Basics->Save & Close.
Set up Notes Routing
To set up routing between servers that are not in the same Notes name network, you must create documents in Domino Directory to specify how to route mail which in the Notes mail system.
(Create connection document to enable message transfer between servers in differern Notes named networks. A connection document specifies how and when two servers connect to exxhange mail and update common database through replication. To route mail between servers in different Notes named networks requires a pair of Connection document, one from each server to the other)
Adjacent Domain
Note:
To define routes between adjacent domains, create a connection documents.
If you deny a domian from sending mail through your domain, the router denies all mail received from that domain, including messages the domain may have passed on from another, non-adjacent domain. There is no way to restrict specific users from routing a Notes Domain, Restrictions apply to all users in specified domain.
DA->Cofiguration->Messaging->Domians->Add Domain->Create a new Domain->Basic complete the proper fields.
Notice
The current Domino domain must have a connection document to this domain.
Non-Adjacent Domain
You can use Non-Adjacent domain to connect to two domain which will supply next-hop domain information.
DA->Cofiguration->Messaging->Domians->Add Domain->Create a new Domain (Select Non-adjacent Domain)->Basic complete the proper fields.
Note: You cannot use wildcards in the restriction fields. You must enter explicit domain names.
By definition , all servers in a domain use the same Domino Directory, only one Non-adjacent domain document is required for each non-adjacent domain. You do not have to create a separate document for each server.
Set up router to external application gateway
Create a Foreign domain document
DA->Cofiguration->Messaging->Domians->Add Domain->Create a new Domain (Select Foreign domian)->Basic complete the proper fields.
Send mail outside the local internet domain
1)Use Relay host
In the configuration settings document that apply to any mail servers that do not connect directly to the Internet, enter the host name of the designated relay host in the "Relay host for messages leaving the local Internet domain" field. When the Router on these internal servers finds a message addressed to a recipient in an external Internet domain, it looks up the specified relay host in the DNS and foreards the message to it.
A relay host is an SMTP server that receives mail form other servers and then transfers. or relays, it to the next SMTP server on the route to the recipient's domain. A relya host can be a Domino SMTP server . or a non-Domino SMTP host
2)Use Foreign SMTP Domain document and an SMTP connection document. (It only can be used between Domino server)
To set this up using Notes protovols, Create a Foreign SMTP Domain document and an SMTP connection document.When the router on a server not connected directly to the Internet find a message address to a recipient in an exteral Internet Domain, the router forwards the message to the Domain in the Foreigh SMTP Domain document, which is connected to the server with an Internet connection by the SMTP Connection document,. When that server receives the message, Its Router connects to the external Internet domain and routes the message.
Notes
If you use a wildcard when specifying which messages to route a domian, you can still restrict messages detined for specific Internet domains using the SMTP Outbound Controls in the Configuration Settings document.
The Router always uses the Foreign SMTP Domain document that most closly match the address. After the Router determins which Foreign SMT Domain document most colosely matches the address of the message, it forwards the message to the specified next domain. If the domain is a real Domino domain. the Router looks in the Domino Directory for a connection to that domain and routes the message. If the domain is a logical domain, the Router checks for an SMTP connection document that describs the next hop for mail routed to that domain.
Create foreign SMTP domain document
DA->Cofiguration->Messaging->Domians->Add Domain->Create a new Domain (Select Foreign SMT domian)->Basic complete the proper fields.
Notice:
Messages Address to Internet Domain: *.*
It means all internet Domain.
Create an SMTP connection document
DA->Configuration->Messaging->connection->Add connection->Basic (Select SMTP)
Source server:The name of the SMTP-enable serverwhere non-SMTP servers send mail destined for the Internet Domains specified in the Foreign SMTP domain document. This server must have access to DNS and have SMTP enabled for sending message outside the local internet domain.
Destination server: A unique, ficitious. placeholder name-- such as all_inernal hosts. Domino does not use the value in this field, but the Connection document will not work if the field is empty. The name you specify must not match the name of any server on ther network.
Destination Domain: The fictitious, logical domain name specified in the internet Domain name field of the corresponding Foreign SMTP domain document. The name in this field links this SMTP connection document with the Foregin SMTP Domain document.
SMTP MTA relay host:
Sepcifies the SMTP host to which the source server transfers outbound mail. This allows a SMTP server to further split internet destinations and configure multiple relays.
If this field is blank, the router transfers outbound mail to the relay host specified in the server's Configuration setting document.
If there is no relay host specified in either this filed ot in the Configuration setting document, the router determines the next hop by looking up the destination domain in the DNS or a local hosts file, depending on the value of "Host name resolution" field on the Router/SMTP- basic tab of the Configuration settings document.
Replication task: Disable
Routing tasl: Mail routing (Because the same routing task is responsible for transferring message over NRPC and SMTP, there's no need to specify SMTP routing. The source server must have SMTP routing enable in it's server document; otherwise, the router discards the information in the SMTP document)
Prepare to send an receive mail to the internet
In some case, a company may have mutiple Internet domain names. Enter thes names as aliases in the Global domain document. And make sure that the DNS is set up to inculde all the Internet domain names that your company uses.
Set up SMTP routing to external Internet domains
DA->Configurations->Configuration settings->Edit Configuration->Touter/SMTP->Basic->Enable "SMTP used when sending message outside the local Internet domain"
rstart router
Set up SMTP routing within the lcoal Internet domain
DA->Configurations->Configuration settings->Edit Configuration->Router/SMTP->Basic-> Select All message on "SMTP allow within the local Internet domain" field.
{SMTP allowed within the local Internet domain
Choose one:
v MIME messages only -- The Router uses SMTP to transfer MIME messages to other Domino servers that are within the same Domino domain and that run the SMTP
Listener.
v Disabled (default) -- The Router uses Notes routing to transfer mail to other servers in the same Domino domain.
v All messages -- The Router uses SMTP to transfer both Notes format and MIME format messages to other Domino servers that are within the same Domino domain and that run the SMTP Listener. This will cause Notes format messages to be converted to MIME format before being transferred. This may cause loss of fidelity and performance. For example, Notes Doclinks will not work.
Note: You can limit the use of SMTP to transfer mail within the Domino domain by
setting the next field (″Servers within the local Domino domain are reachable via
SMTP over TCPIP″) to only allow SMTP within the same Notes named network.
Servers within the local Domino domain are reachable via SMTP over TCPIP
v Always (default) -- The Router can use SMTP to transfer mail to any Domino server in the local Domino domain that runs the SMTP Listener.
v Only if in same Notes named network -- The Router can use SMTP to transfer mail to other Domino servers in the local Domino domain only if the destination server is in the same Notes named network. If the destination server is in the local Domino domain, but resides in a different Notes named network, the Router must use Notes routing to transfer mail.}
Enable a server to receive mail send over SMTP routing
DA->Configuration->Server->select server document->edit server->Basic
Fully qualified internet host name:
In the absence of a Global Domain document, the router use the entry in this field to determine the local Internet domain. Typically, the fully qualified host name is added to the server document during server setup or by the Administration process. A routing loop can result if this field does not contain a valid entry.
Click Ports->Internet Ports->Mail
In the Mail (SMTP Inbound) colum,ensure that the TCP/IP port status is set to Enable, and then click "Save and Close"
SMTP listener task: Enable
Set up how address are resovled on inbound and outbound mail
Set up s smart host
DA->Configurations->Messaging->Configurations->Edit configuration->Router/SMTP->Basic
Local Internet domain smart host
The host name for the serve that hosts the directory for SMTP recipients who are not in the Local Domino Directory. To provide a level of failover and load-balancing, specify a host name that maps an existing MX record. You can also specify IP address.
Note:
If this field contains a host name entry and the field "Verify that local domain recipients exit in the Domino Directroy" is enabled, messages addressed to local recipients that can not be resoved are not accept; thereore, there is no transfer of messages to the smart host.
Smart host is used for all local Internet domain recipients:
Choose one:
v Enabled to route all incoming SMTP messages to the smart host for lookup before routing elsewhere.
v Disabled (default) to route only messages whose recipients are not found in the Domino Directory to the smart host for lookup.
Note: If this field is set to Enabled, and the field ″Verify that local domain recipients exist in the Domino Directory″ is enabled, messages are received only for recipients whose names can be resolved in the Domino Directory. If this field is set to Enabled, and messages are accepted, all of these messages for local recipients are forwarded to the smart host.
Set up a server to receive mail for multiple internet domains
Create a Global Domain document
DA->Configuration->Messaging->Domain->Add Domain->Global Domain->Basic
Complete the proper fields.
Domain type: Global Domain
Global domain name: (optional) A word or phrase that describes the domain. Never use the name of an existing domain for your Global Domain.
Domino domains and aliases: The Domino domain name and aliases. Domino uses the domain name and aliases when accepting mail from the alternate domains list in the Global domain document.
Conversion tab
Local primary Internet Domain:
The primary Internet domain: The primary Internet domain name that your company uses to represent themselves to the outside world.
Alternate Internet domain aliases:
Addtional Internet domain names that your company uses
Use the asterisk (*) as a wildcard to represent the names of subdomains. Wildcard use is valid only if the wildcard character appers as the first character of a given entry and represents an entire subdomain name, for example:the entry *.another.com indicats that Domino treats any subdomain of "another.com" as a local domain.
Specify how Domino looks up the recipients of incoming SMTP messages.
When Domino receives a message over SMTP, the message recipient is identified by an Internet-style address. To determine the correct destination mail file, Domino must match the SMTP address to a person document in the Domino Directory (The directroy files is names.nsf), To find a match , the router checks the $Users view of the directory. This view displays all name entries in all Person documents in the directory, inculding Internet mail addresses, as well as all user name variations, firstl names, last names, common names (CN) distinguished names (DN), short names, and soundex names.
Note:
To display the hidden $Users view: Open the directory (open names.nsf), press CTRL-SHIFT and select View->Go TO dialog box, select the view ($User) and click OK.
Inbound recipient lookups adr controlled by the Address lookup setting on the Router/SMTP->"Basic of the Configuration settings" document. This settings determines the criteria that the Router uses hen attempting to match the SMTP address on an incoming message to an entry in the $User view.
The Router matches addresses based on:
The full SMTP address only
The local part of the SMTP address (That is, the part to the left of the @ sign) only
The full SMTP address, and then if no match is found , the local part address
To specify how address are looked up
DA->Configuration->Messaging->Configurations->Router/SMTP->Basic
Exhaustive lookup: Enable - The router seraches all directories to ensure that there are no duplicate recipient names that might prevent the message from getting to the right person Performing exhaustive lookups is time0conduming and places a heavy load on the server.
Set how host names are looked up
DA->Configuration->Messaging->Configurations->Router/SMTP->Basic
Host name lookup Choose one:
Dynamic lookup only (DNS only) - The Router determines the IP address for a host by looking it up in DNS. SMTP transfer can occur only if the destination host is listed in DNS.
Local lookup only (host files only) - The Router determines the IP address for a host by looking it up in a hosts file on the local machine.
Dynamic then local - (default) The Router determines the IP address for a host by looking it up in DNS first and then checking the local hosts file if no DNS entry exists.
Enable the router to look up the sender's internet address from the person document
If the sending user’s Location document specifies an Internet address, Domino places this address in the From field of the MIME message. However, if the Location document does not specify an Internet address, Domino must obtain the address by other means. By default, Domino forms an Internet address by converting spaces in the user’s Notes address into underscores, and prefixing the names of Domino domains in the address with percent signs. For example, a Domino server in the acme.com Internet domain converts the Notes address John Smith@Notes to the Internet address John_Smith%Notes@acme.com. Domino determines the Internet domain from the Server document or the Global Domain document
DA->Configuration->Messaging->Configurations->MIME->Conversion Option->Outbound
Lookup Internet address for all Notes addresses when Internet address is not defined in document:
Addresses on all messages sent to Internet recipients must be in Internet format
(RFC 821/822 format). A Notes user may send a message to both Notes addresses
and Internet addresses. To specify how Domino converts the addresses of Notes
recipients on messages sent to the Internet, choose one:
v Enabled - On outbound Internet messages, if the address of the sender or any recipient is in Notes format, Domino looks up the user’s Internet address from the Person document and, if found, substitutes it for the Notes address before sending.
v Disabled - (default) Domino forms Internet addresses based on rules in the Global Domain document. If a Global domain document is not present, Domino constructs addresses by converting spaces into underscores and encoding Domino domains with percent signs. For example, Domino converts the Notes address John Smith@Notes to the Internet address John_Smith%Notes@acme.com
Note: When this option is disabled, Domino will continue to perform Internet address lookups if configured to do so in the field ″Internet address lookup″ in the SMTP Address Conversion section of the Conversion tab of the Global Domain document.
If the Router cannot obtain the sender’s Internet address from either the message itself or the Person document, it will construct the address. You can specify the rules for constructing this address in the Global domain document, but in the absence of a Global domain document, the Router constructs Internet addresses using the following default format:
Full_Name/Org%DominoDomain@IPDomain.TopLevelDomain
How Domino uses Global domain documents during inbound and outbound SMTP routing
When Domino receives an inbound SMTP message, it attempts to determine whether the message is for a local recipient. When the Domino Directory does not include a Global Domain document, Domino accepts only messages addressed to users in the same Internet domain as the server, as indicated in the Fully-qualified Internet host name that appears in the Server document. But if the Domino Directory includes a Global domain document, Domino can receive mail for multiple Internet domains. To determine whether to accept a message, Domino compares the domain part to the local primary Internet domain listed in the Global domain document. If it does not find a match in this field, it examines the secondary Internet domains -- the ″alternate Internet domain aliases″ -- listed in that
document.
The role of Global domain documents in determining whether to accept inbound SMTP mail: If the Domino Directory contains multiple Global domain documents, Domino uses a similar process todetermine whether a recipient is local: it first checks the primary Internet domain in each Global Domain document, and then, if it still hasn’t found a match, it continues by checking the alternate Internet domains. If the domain in the address does not match any of the domain entries in any Global domain document, the message is considered an attempt to relay, and Domino rejects the message.
Inbound address lookup when the Domino Directory contains multiple Global Domain documents:
After Domino accepts a message, the Router attempts to match the recipient’s Internet address to an entry in the Domino Directory. When looking up the recipient in the Domino Directory, if the domain suffix in the address matches an alternate Internet domain aliases defined in a Global Domain document, and no Person document includes this address, the Router performs a secondary lookup. In this secondary lookup, the Router pairs the local part of the address with the domain suffix of the primary Internet domain specified in the Global domain document. For example, a server receives a message for craig_bowker@acmewest.com. The Router searches all of the Person documents in the Domino Directory for this Internet address, but cannot find a match. However, in the Domino Directory, there is a Global domain document that includes the domain suffix
acmewest.com as an alternate Internet domain alias. In this same Global Domain document, the primary Internet domain is acme.com. After the primary lookup fails, Domino performs a secondary lookup, using the address craig_bowker@acme.com. Domino performs secondary lookups only if the Router is configured to perform fullname, or fullname, then local part lookups. In cases where the Domino Directory contains multiple Global domain documents, and a secondary lookup is required, when replacing the domain suffix in the original address with the domain suffix of the primary Internet domain, the Router only considers Global domain documents that list the alternate Internet domain alias. That is, Domino always replaces the domain suffix from within a given document;
it never replaces an alternate domain listed in one document with a primary domain from another document. To prevent the Router from using domain aliases when looking up addresses, do not include alternate Internet domain aliases in a Global domain document. Instead, create multiple Global Domain documents, each specifying a different primary Internet domain.
Controlling outbound addresses construction with multiple Global domain documents: When the Domino Directory contains a single Global Domain document, the address construction rules in that document determine how a server forms the sender’s address in an outbound SMTP message. However, if the Domino Directory contains multiple Global Domain documents, when constructing the sender’s address, Domino uses the Internet domain specified in the Server document and the address construction rules defined in the Global Domain document listed last, alphabetically, in the directory. If you want Domino to form the sender’s outbound address from the primary Internet domain and the address construction rules contained in a particular Global domain document, designate that document as the default Global Domain document.
Designating a default Global domain document:
When there are multiple Global Domain documents in the Domino Directory, designate one as the default so that when a servers construct a sender’s outbound Internet address, the addresses created are based on the primary Internet domain and address construction rules specified in the designated document.
1. From the Domino Administrator, click the Configuration tab and then expand the Messaging section.
2. Choose Domains, and click Global Domain
3. Select the Global Domain document you want to designate as the default and click Edit Domain.
4. On the Basics tab, complete following field, and then click Save & Close
Use as default Global Domain (for use with all Internet protocols except HTTP)
Select Yes to designate this Global Domain document as the default Global
domain for this Domino Directory.
Update the SMTP configuration
The SMTP service controls the SMTP listener on the Domino server. By default, whenever you restart the SMTP service, and at two-minutes intervals thereafter, the SMTP service automatically checks the Notes.ini filr. Configuration settings document, and Server document to see if any settings have changed. If the service detects that settings have changed. it rebulids its internal cofiguration to incorporate the changes.
You can use a server console command to manually trigger such a service update, Using the console command allows you to immediately put into effec changes to the SMTP configuration without disrupting normal service operation.
To update the SMTP service configuration
1)Modify settings in the Notes.ini, configuration settings document, or server document
2)Run Tell smtp update config.

没有评论:
发表评论